SQL Server provides the concept of temporary table which helps the developer in a great way.

- These tables can be created at runtime and can do the all kinds of operations that one normal table can do.
- But, based on the table types, the scope is limited.
- These tables are created inside tempdb database
Different Types of Temporary Tables
SQL Server provides two types of temp tables based on the behavior and scope of the table. These are:
- Local Temp Table
- Global Temp Table
Local Temp Table
Local temp tables are only available to the current connection for the user; and they are automatically deleted when the user disconnects from instances. Local temporary table name is stared with hash ("#") sign.
Global Temp Table
Global Temporary tables name starts with a double hash ("##"). Once this table has been created by a connection, like a permanent table it is then available to any user by any connection. It can only be deleted once all connections have been closed.
Local Temporary Table
The syntax given below is used to create a local Temp table in SQL Server 2005:
Hide Copy Code
CREATE TABLE #LocalTempTable(
UserID int,
UserName varchar(50),
UserAddress varchar(150))
The above script will create a temporary table in
tempdb database. We can insert or delete records in the temporary table similar to a general table like:
Hide Copy Code
insert into #LocalTempTable values ( 1, 'Abhijit','India');
Now
select records from that table:
Hide Copy Code
select * from #LocalTempTable
After execution of all these statements, if you close the query window and again execute
"Insert" or "Select"Command, it will throw the following error:
Hide Copy Code
Msg 208, Level 16, State 0, Line 1
Invalid object name '#LocalTempTable'.
This is because the scope of Local Temporary table is only bounded with the current connection of current user.
Global Temporary Table
The scope of Global temporary table is the same for the entire user for a particular connection. We need to put
"##" with the name of Global temporary tables. Below is the syntax for creating a Global Temporary Table:
Hide Copy Code
CREATE TABLE ##NewGlobalTempTable(
UserID int,
UserName varchar(50),
UserAddress varchar(150))
The above script will create a temporary table in tempdb database. We can
insert or delete records in the temporary table similar to a general table like:
Hide Copy Code
insert into ##NewGlobalTempTable values ( 1, 'Abhijit','India');
Now select records from that table:
Hide Copy Code
select * from ##NewGlobalTempTable
Global temporary tables are visible to all SQL Server connections. When you create one of these, all the users can see it.
Storage Location of Temporary Table
Temporary tables are stored inside the Temporary Folder of
tempdb. Whenever we create a temporary table, it goes to Temporary folder of tempdb database.
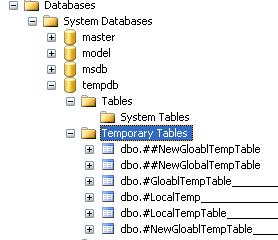
Now, if we deeply look into the name of Local Temporary table names, a '
dash' is associated with each and every table name along with an ID. Have a look at the image below:
SQL server does all this automatically, we do not need to worry about this; we need to only use the table name.
When to Use Temporary Tables?
Below are the scenarios where we can use temporary tables:
- When we are doing large number of row manipulation in stored procedures.
- This is useful to replace the cursor. We can store the result set data into a temp table, then we can manipulate the data from there.
- When we are having a complex
joinoperation.
Points to Remember Before Using Temporary Tables
- Temporary table created on
tempdbof SQL Server. This is a separate database. So, this is an additional overhead and can causes performance issues. - Number of rows and columns need to be as minimum as needed.
- Tables need to be deleted when they are done with their work.
Alternative Approach: Table Variable
Alternative of Temporary table is the Table variable which can do all kinds of operations that we can perform in
Temp table. Below is the syntax for using Table variable.
Hide Copy Code
Declare @TempTableVariable TABLE(
UserID int,
UserName varchar(50),
UserAddress varchar(150))
The below scripts are used to
insert and read the records for Tablevariables:
Hide Copy Code
insert into @TempTableVariable values ( 1, 'Abhijit','India');
Now select records from that
tablevariable:
Hide Copy Code
select * from @TempTableVariable
When to Use Table Variable Over Temp Table
Tablevariable is always useful for less data. If the result set returns a large number of records, we need to go for temp table.
Ref : https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/42553/Quick-Overview-Temporary-Tables-in-SQL-Server
Comments
Post a Comment